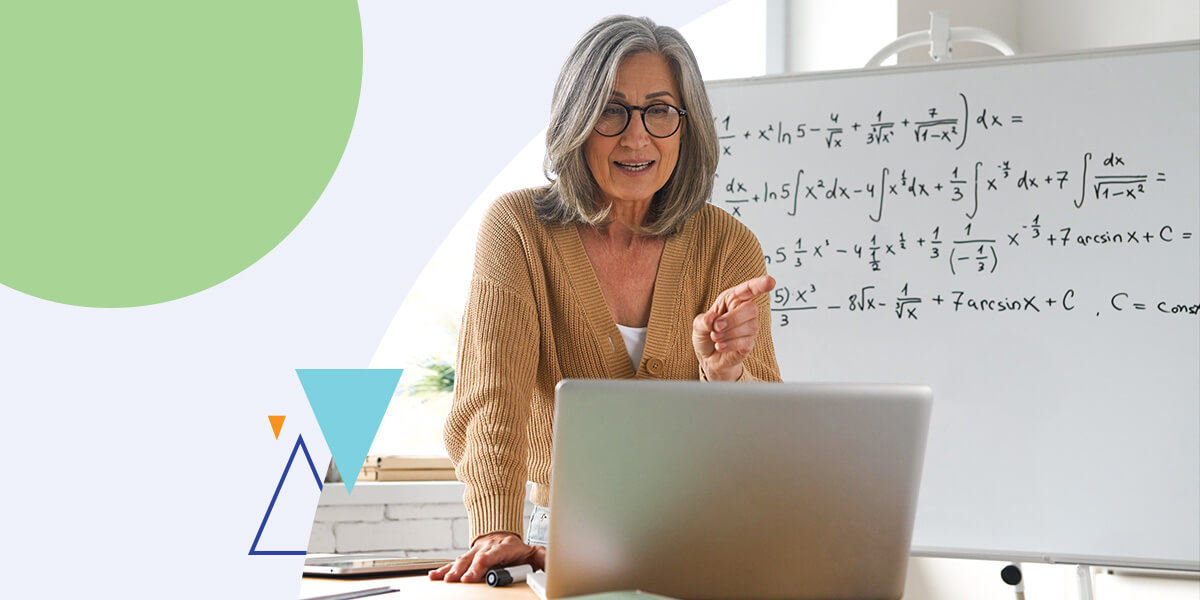
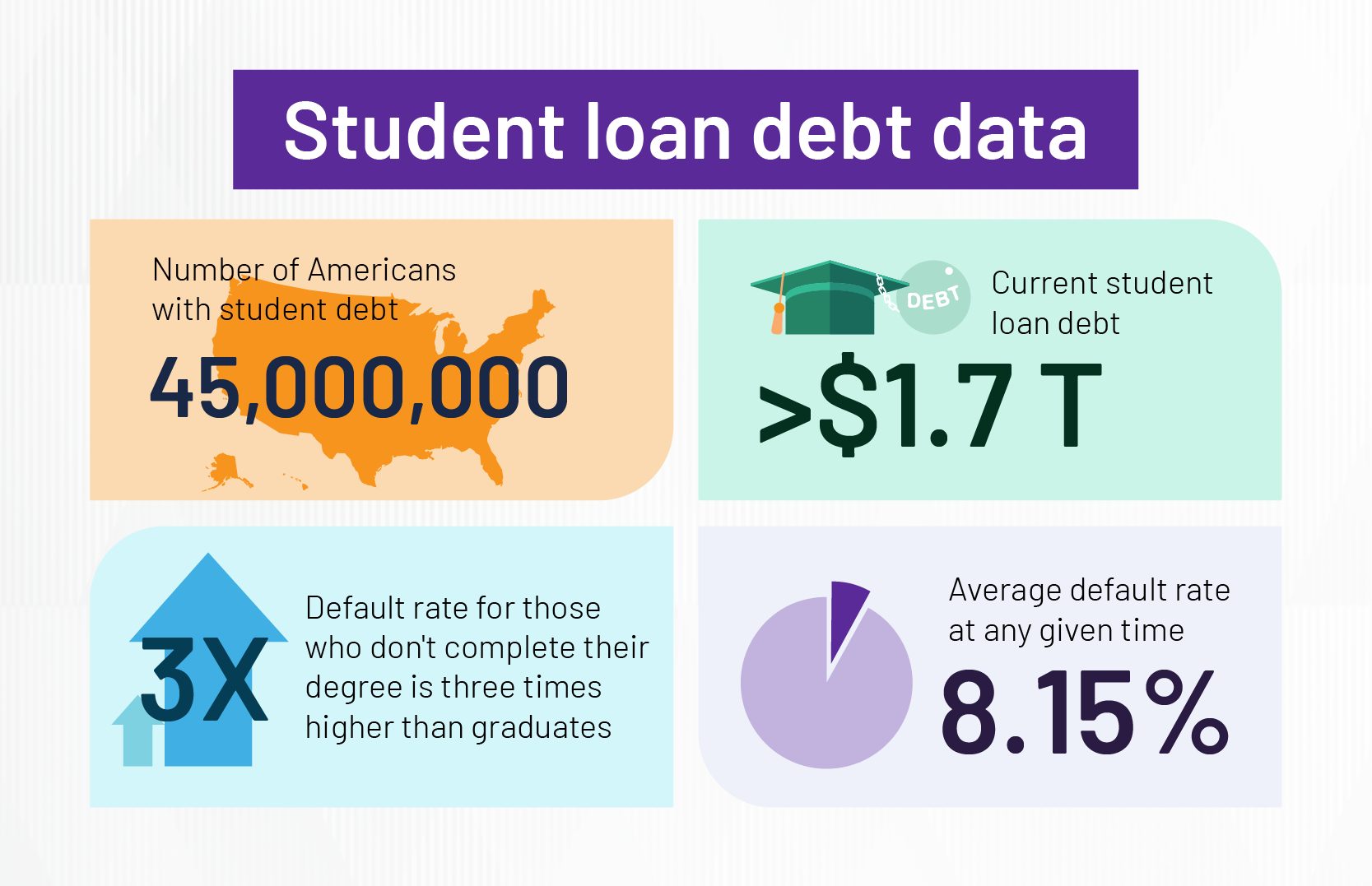
The importance of academic freedom in higher education cannot be overstated. It ensures that individual faculty members can design their courses, research, and innovate. It means faculty and students can engage in intellectual debate without fear of censorship or retaliation.
Aside from being a fundamental premise in higher education, academic freedom promotes societal innovation. Without it, many breakthroughs in fields like science, humanities, and social justice wouldn’t exist.
Academic freedom is the freedom of teachers and students to teach, learn, and pursue knowledge and research. They can do so without unreasonable interference or restrictions from law, institutional regulations, or the public. In today’s higher education landscape, the academic freedom of faculty members is more important than ever. It maintains the rights of institutions to operate without government or societal pressure, but beyond that, it also boosts student and faculty success.
Understanding academic freedom in higher education
Medieval institutions of higher education laid the foundation for this freedom when they became legally self-governing organizations. Although academic freedom is never without some limitations, faculty should have the right to teach without government sanction.
Throughout the 20th century, academic freedom came to mean the protection of faculty and institutional neutrality from outside political sources. It involved policing the line between knowledge and partisanship. Today, it still protects intellectual freedom. It protects the rights of faculty and students to their views and ideas, allowing both parties to thrive in an academic environment.
Academic freedom is essential for individual success in higher education and plays a vital role in shaping society’s future. It allows faculty to research pressing societal issues such as environmental changes, public health, and human rights. The truths they uncover may be inconvenient or controversial, but they are crucial for society to progress.
The pillars of academic freedom
Academic freedom affects more than higher education institutions. It benefits society as a whole. Society flourishes when the educational process leads to the advancement of knowledge, and knowledge is best advanced when inquiry is independent. For students, it means the freedom to study subjects that concern them. For faculty, it means they can teach in a manner they consider appropriate and publish their data without control or censorship.
The four pillars of academic freedom include:
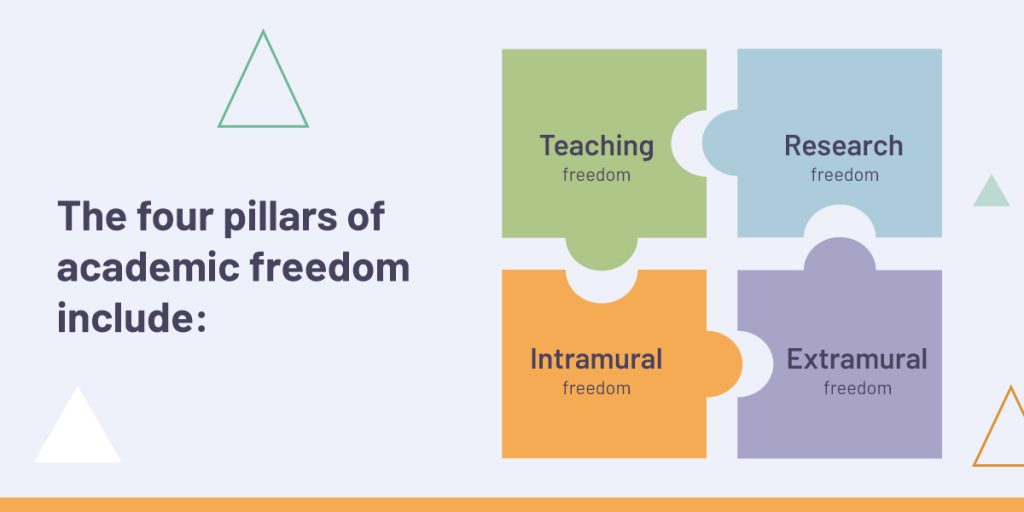
- Teaching freedom: Academic staff must be free to exercise their professional judgment and expertise about what and how to teach. They can organize course content and activities, assess and evaluate student performance, and select pedagogical material. They can also assign educational material without fear of external interference. When faculty can educate freely, students benefit from their passion, engagement, and autonomy.
- Research freedom: The foundation of higher education institutions is to advance knowledge through the freedom of academic staff to pursue and share research. They have the freedom to speculate, investigate, and share the results of their research. Institutions must ensure their staff are unimpeded in their research, free from outside influence, pressure, and attempts to limit publication. Current and future students can only benefit from attending an institution that spearheads diverse and meaningful research.
- Intramural freedom: Intramural freedom gives academic staff the right to comment on and participate in policy and governance. Institutions aiming for academic freedom must integrate their faculty in all aspects of academic life, including meetings and informal discussions. It allows faculty to collaborate and engage, which, in turn, benefits students.
- Extramural freedom: Extramural freedom gives academic staff the right to express their views freely. They can speak freely within their expertise on matters of public interest. It allows for free content, debates, and discourse among academic staff.
Academic freedom as a driver of faculty success
Academic freedom empowers faculty members to pursue their unique ideas without fear of backlash, promoting the exploration of new knowledge. It also protects the diversity of perspectives and approaches that enrich the academic community. With the freedom to pursue research and engaging curricula, faculty can express their ideas and pursue their success.
When faculty have academic freedom, students benefit. Faculty members create a safe space for students to learn, allowing them to explore every perspective of a topic and draw their own conclusions.
As pedagogical freedom makes teaching positions more attractive, intellectual freedom makes learning more engaging and personal for students. When faculty can express themselves freely, they bring a unique passion and inspiration to their teaching. They create a space where students can explore, make subjects relevant to their lives, and ultimately succeed.
The correlation between faculty autonomy and research innovation
Academic freedom encourages faculty members to question existing paradigms and tackle complex research issues. It brought forth revolutionary concepts in many academic domains and continues to support critical thought and progressive research today. Higher education institutions are under increasing pressure to seek outside funding for research. Academic freedom has strong positive effects on the quality and quantity of innovation output in institutions.
One study showed that an improvement in academic freedom by a single standard deviation increased the number of patent applications two years later by 41 percent. The positive relationship between academic freedom and invention is integral to institutional and student success. In addition, creating safe spaces to air opinions encourages faculty to collaborate. It allows research to be born from diverse perspectives — an essential element of academic innovation.

The role of academic freedom in faculty career satisfaction
Academic freedom is nonnegotiable for many faculty members. It allows them to remain true to their pedagogical philosophies and intellectual commitments. It allows them to study and research the topics they choose, allowing them to innovate and follow their calling. In addition, it provides protections that many faculty members seek when establishing careers at higher education institutions. Academic freedom allows them to seek redress if they believe their rights have been violated. It also protects them from reprisals for disagreeing with administrative proposals or policies.
This autonomy is essential for overall faculty success and career development. When an institution implements programs that support academic freedom and faculty development, it also attracts top talent. This creates a cycle where faculty feel comfortable innovating, growing their careers, and benefiting their students.
Academic freedom and curriculum development
Academic freedom directly impacts how faculty present information to students and map curricula. Curriculum mapping is crucial for aligning educational content with desired outcomes, including preparing students for meaningful careers. When faculty are free to adapt learning for student success, they can shape dynamic and relevant curricula that engage students. In doing so, they facilitate student success.
Faculty play a pivotal role in building academic freedom while maintaining educational consistency. When collaborating in mapping curricula, they can adjust in real time to meet changing student needs. This process begins with curriculum mapping, allowing faculty to align their programs with what students are expected to know and do at the end of their academic journeys.
The impact of curriculum mapping of education quality
Curriculum mapping elevates education quality in several ways. It aligns educational programs with the learning and skills students need to succeed. It gives institutions a bird’s-eye view of their curricula, allowing them to analyze and organize them to benefit students. It also creates a connected learning journey for faculty and students. Through curriculum mapping, higher education institutions can align their programs with academic standards, accreditation requirements, and industry expectations, all while maintaining academic freedom.
This tool does more than create a cohesive learning journey. It allows faculty to approach topics freely while ensuring students hit the necessary milestones to proceed through their education. Institutions can track expected and actual outcomes to measure student success in courses. Measuring learning outcomes allows institutions to determine how effectively courses meet learning objectives. After a course is complete, they can improve what is taught in the classroom and how — the perfect balance between freedom and consistency.
Measuring success through academic freedom
Academic freedom means that institutions can measure student success beyond test and exam results. Instead, courses are relevant to students. Student success is much more complex than academic results. It includes social and psychological dimensions. As academic freedom meets faculty needs to express themselves and pursue areas of study that interest them, it does the same for students.

Some of the benefits of academic freedom for student success include:
- Collaboration in classrooms: Students from diverse backgrounds can participate in class discussions and share their opinions openly. Students feel empowered to engage in debate, actively valuing all voices and contributors. This collaboration fosters critical thinking and problem-solving in students and prepares them for the working world.
- Relevant curricula: Every faculty member has a different viewpoint and teaching style. Two people teaching the same subject matter may approach it from entirely different angles. These differing interpretations give students a relevant and comprehensive understanding of the subject.
- Mental health support: A climate of academic freedom can support the mental health and well-being of students. It creates an environment where they feel safe to express themselves, which can improve their academic performance.
- Creativity and innovation: When institutions encourage students and faculty to think outside the box and take intellectual risks, they can innovate and problem-solve in a way that complements today’s rapidly changing job market.
- Personalized learning experiences: Academic freedom allows faculty to tailor their teaching methods and course content better to meet the unique needs and interests of students. This approach enhances engagement, boosts student success, and connects their learning with their personal and professional goals.
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion: Academic freedom creates an environment where marginalized voices can be heard. It empowers underrepresented groups to engage in scholarship and advocacy, addressing systemic inequalities. Institutions that prioritize academic freedom are better equipped to create culturally responsive curricula, reflecting different perspectives and histories. Making course material relevant to students can enhance student engagement and success as they see their experiences and identities reflected in the classroom.
Challenges facing academic freedom
In today’s unpredictable higher education climate, academic freedom faces several challenges:
- Political and governmental pressure: Policies and political ideologies can restrict academic freedom in some states. Academics who contradict certain narratives may face censorship or funding cuts.
- Self-censorship: Faculty and students may censor their ideas and research topics for fear of backlash, negative responses, and social consequences. They may refrain from exploring new subjects, hampering an institution’s ability to innovate.
- Social and cultural backlash: In today’s polarized society, faculty and students who engage with controversial topics may face backlash from social and cultural groups. It can manifest as threats, protests, or public campaigns, creating a toxic academic environment.
- Data privacy concerns: The rise of technology and digital platforms has made it easier for institutions to gather data and monitor student and faculty activities. While this data gives institutions the power to improve, concerns about data privacy could limit free expression.
How institutions can safeguard academic freedom
Academic freedom is critical for faculty, students, higher education institutions, and society. Institutions looking for ways to protect it and improve student outcomes can implement the following steps:
- Have a plan: Institutions that know what’s happening on their campuses and states can address any threats to academic freedom. They can issue climate surveys to reveal real-time insights from students and faculty. They can also establish campus forums to maintain open communications on academic freedom.
- Track student success: Academic freedom for faculty should never come at the expense of students. Gathering student data into actionable insights can help institutions identify students falling behind and intervene at the right time.
- Map the curricula: Outlining transparent and interconnected curricula for each program helps faculty and administrators focus on achieving the appropriate student outcomes. It also allows them to identify curriculum gaps and growth areas to adapt programs in real time to meet student needs.
- Support diverse research and teaching: Institutions can take proactive steps to integrate culturally responsive and varied education and allocate funding for innovative research projects and multifaceted research offerings.
Measure student success with Watermark

Academic freedom is a powerful force in higher education.
It’s even more powerful when you can map your curricula and measure the results. With Watermark Curriculum Strategy, you can collaborate and share a curriculum that powers student success and maintains academic freedom. Make your students part of the journey by using their feedback to inform curricular changes and map your processes with visual workflows.
Watermark Curriculum Strategy is part of our complete Educational Impact Suite (IES), which is purpose-built for higher education. This integrated hub of tools puts your data into context. It gives you the big picture to drive meaningful change in every aspect of your institution. With effortless insights, you can foster continuous improvement that supports faculty success and engages students. Request a demo today to learn more about our solutions!